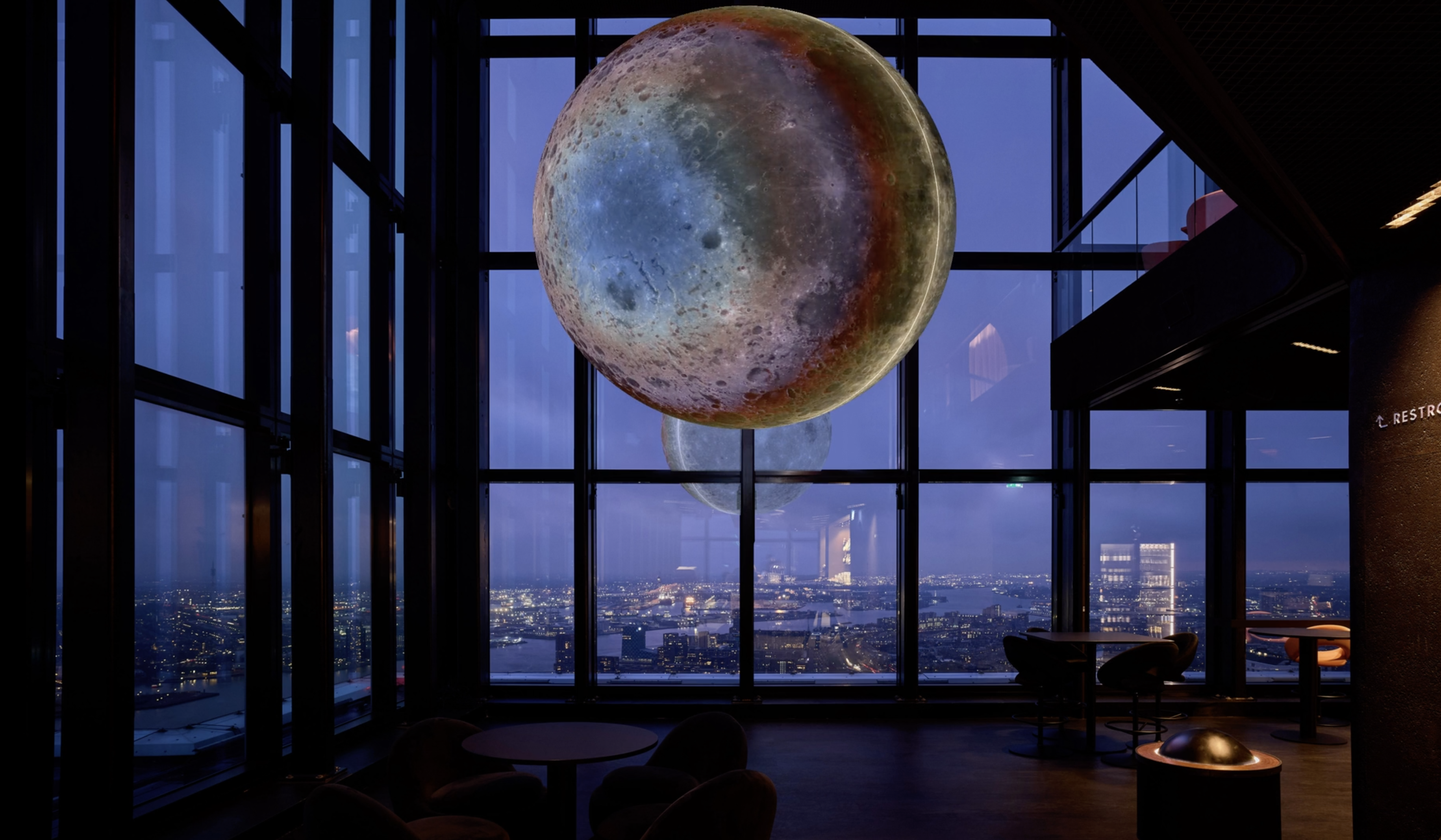
Fleets of self-driving cars will help to solve traffic problems in cities in the long term. These benefits become even more apparent when coupled with smarter traffic management and a higher occupancy rate, i.e. increasing the average number of persons per car. If this figure rises moderately from 1.1 to 1.3 persons, because more people share a car, there is no more congestion during rush hour. In a fully automated, networked traffic system, more people (+12%) can be transported much more quickly (-33%) in commuter traffic.
How much time will we save in a city with autonomous cars, ride sharing and smart traffic management? The "25th Hour: Flow" project by Audi tries to answer these questions by partnering with traffic experts at the Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT), MobilityPartners and RNDR.
Connected, automated and shared vehicles also provide cities with new opportunities to use and reallocate space to improve urban quality of life. For example, the study found that the incorporation of fully autonomous vehicles could repurpose one traffic lane in a four-lane network and dedicate this new space to pedestrians or bicycles instead of vehicles. The study takes into account that, with an increasing number of autonomous cars, more senior citizens and children without a driver’s license have access to mobility, and convenient robo-taxis will compete with local public transportation.
The results suggest that autonomous cars, mobility services, and networked infrastructure can significantly reduce congestion and road space. At the same time, more young and old people can travel safely and conveniently. In this way, the quality of life in cities will be improved dramatically. These findings encourage us to continue our investment in the future: in self-driving cars, on demand services, or networked technology such as traffic-light information.
The study also examines more extreme scenarios. For example, what happens if there is a sharp increase in the number of people who use public transportation, walk, or travel by bike? What is the effect of high levels of delivery traffic as a result of online shopping? And what happens if cities do not permit self-driving cars or are slow or reluctant to digitalize their infrastructure? The results range from shorter journey times in commuter traffic (-40%) to gridlock.
“The effects of connected and automated vehicles and of other technical and societal developments are continuously studied in the transportation research community. In most cases, the studies focus on single aspects of these developments in order to better identify the isolated effect of exactly that aspect alone. Our objective was different: We wanted to draw a picture of what mobility will look like when all these effects come together,” says Professor Peter Vortisch, head of the Institute for Transport at the KIT.
In the traffic model for Ingolstadt, the researchers investigated only one parameter in isolation, without taking account of changes in user behaviour or increased demand: how many self-driving cars would be needed today to make the traffic flow noticeably better? At least 40 percent! Computers maintain the necessary distance to other vehicles, do not drive too fast, and obey all traffic signals. However, according to several academic studies, in a mixed traffic situation this has a disadvantage for traffic flow. Journey times are noticeably cut only with an increasing number of autonomous cars: if the roads in Ingolstadt today were used only by autonomous vehicles, travel times would fall by one quarter.
Audi’s 25th Hour project
Today, on average, drivers spend about 50 minutes per day at the wheel. In the 25th Hour project, since 2017 Audi has been investigating how self-driving cars will change our everyday lives. In the future will we continue to spend almost an hour a day in the car?
In addition, the traveling time in the self-driving car can be put to good use: passengers talk, relax or work. In collaboration with the Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Engineering (IAO), Audi investigated how, for example, the interior of the car can become a perfect workplace.
Digitalisation and urbanisation transform cities, mobility and user behaviour. Automobile concepts, however, are being developed today – and have to blend smartly and efficiently with developing mobility systems in the future.
Studio
RNDR is a design studio for interactive media that develops ‘tools’ that are only finished by how they are used.
To achieve this, we develop processes, create structures, design visualisations, code programs, and create interactions. The end result can manifest itself across different media, ranging from interactive installations, data visualisations, generative identities, prints and everything in between – often real-time. We are triggered by how information and technology transforms networks, cultures, societies, relationships, behaviours, and interactions between people. Our work explores and engages with hybrid space as it embraces both digital and physical realms.
RNDR was founded in 2017 in The Hague, (NL). Its main members have years of experience as partners, computer scientists, designers, art directors and developers at LUST and LUSTlab.
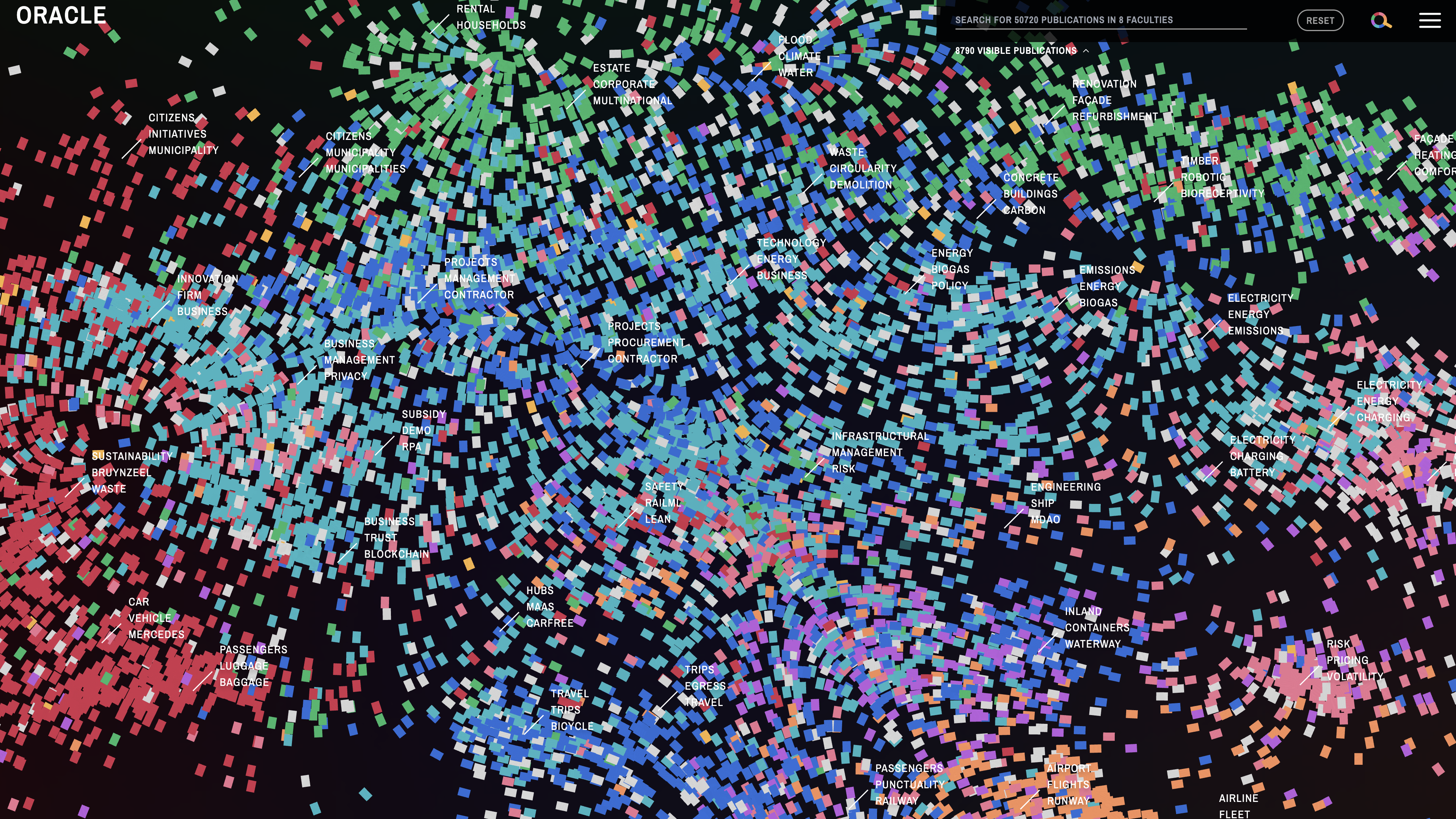
One of our core projects, and basis for most of our projects, is OPENRNDR, an open source framework for creative coding –written in Kotlin for the JVM– with over 13 years of development. OPENRNDR simplifies writing real-time audio-visual interactive software. OPENRNDR is fundamental for the capacity of RNDR as a studio, as it allows us to realize complex interactive works. OPENRNDR was awarded the Dutch Design Award 2019.
Fields of work
Interactive design (ui/ux), data visualisation, information systems, software tools, interactive installations, media architecture, immersive experiences, interface design, visual identities, generative video, creative coding, exhibition design, graphic design systems, hybrid spaces and platforms, machine learning and artificial intelligence (ai), code and design workshops.
We have worked for or collaborated with
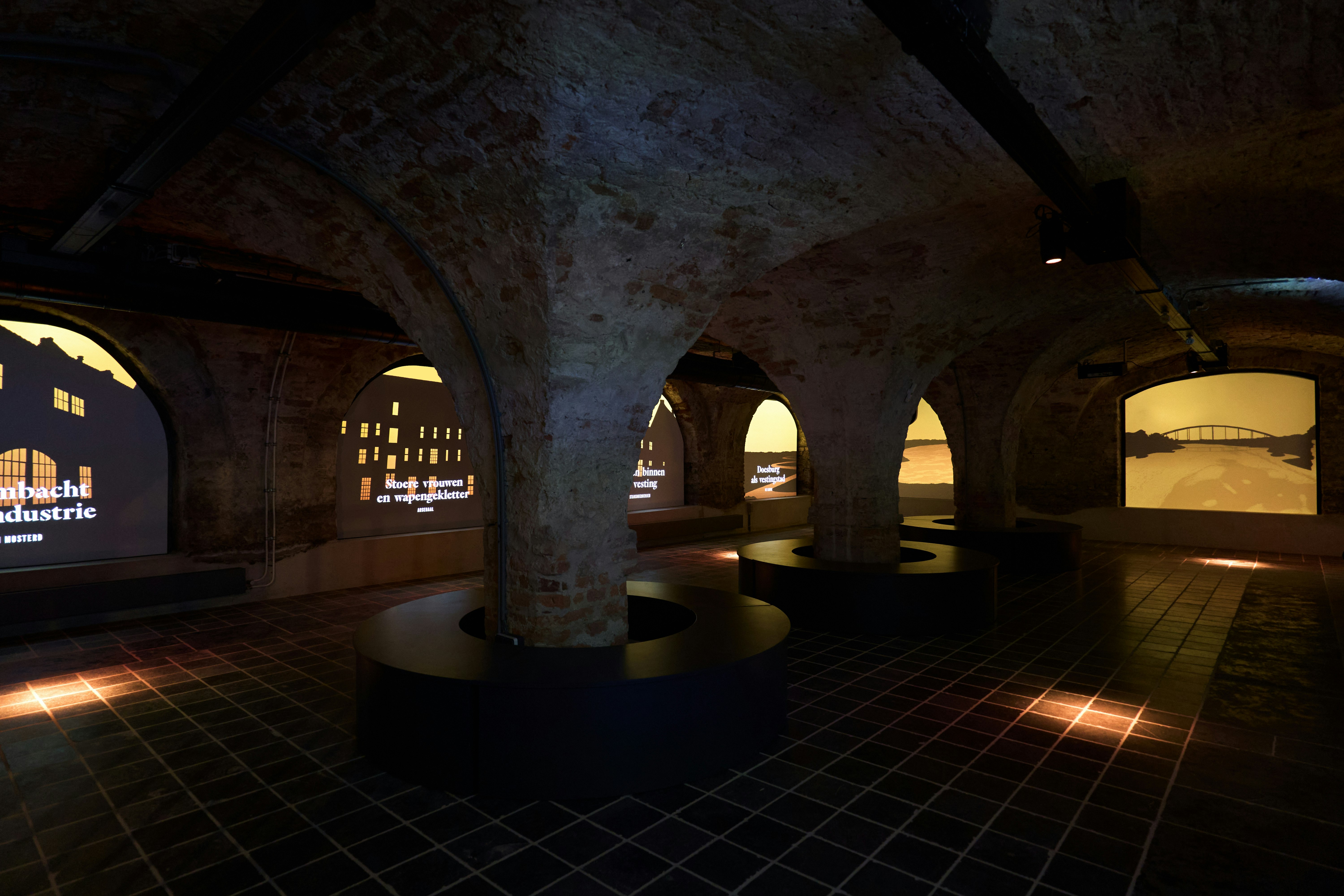
Philips, Audi, Massive Attack, Foto Museum, Autostadt, Stedelijk Museum Amsterdam, DropCity, Google, MoMA New York, IABR, VNG, DoepelStrijkers Architects, Kaan Architects, Buchmesse Frankfurt, European Environment Agency, PARC, Government Summit Dubai, RAP, Technical University Twente, Royal Holloway University, Paradox, Space10, Cooper Hewitt, Hammer Museum, Jacquemus, Holland Festival, RAUM, Civic Architects, The Municipality of The Hague, Vlisco, Police Emergency Center, KPN, Tod’s, Zegna, LI-MA, WTTC, Institute for Future Cities, Makropol, IDFA, UCLA, Artez Arnhem, Ministry of Internal Affairs, Digital Society School, Andrea Caputo Architects, Doesburg vertelt, VNG, Wellcome Trust, Ministry of Economic Affairs, NOI Tech Park, CELEST, Electric Castle, and many more.
Contact
RNDR
Paviljoensgracht 20
2512 BP, The Hague
+31 (0)70.3635776
INTERNSHIPS
Currently, we don’t have any open internship positions or job openings. We appreciate your interest, and we encourage you to check back with us in the future.
OPENRNDR
Open source framework for creative coding that simplifies writing real-time interactive software